Technology
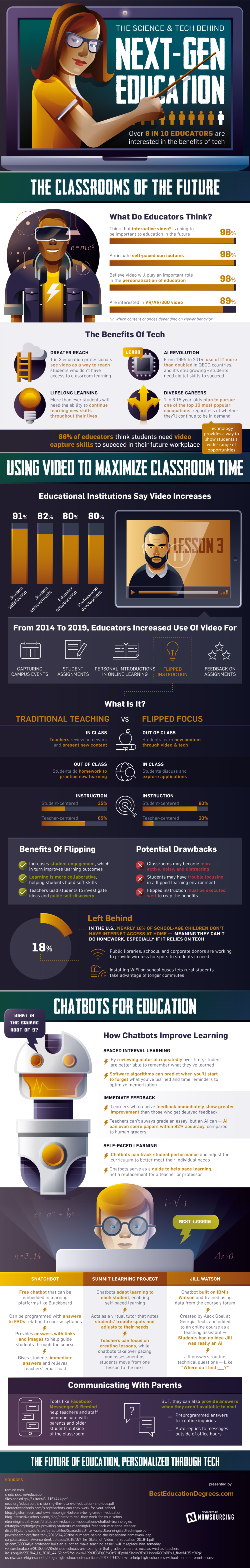
How Technology is Shaping the Future of Education
Technology has transformed almost every aspect of our lives, and now it seems that education systems around the world are due for an update.
Educators are tapping into the digital revolution and adopting new technologies to help students reach their full potential, but can they adapt quickly enough to prepare children for the changing future of work?
The Growing Role of Tech in Classrooms
Today’s infographic from Best Education Degrees explores the different ways technology is transforming classrooms, and disrupting education as we know it.
The Next Generation
Although some might view technology as pervasive, for younger generations, it is ever-present.
Children and young adults make up one-third of all internet users, so it’s no surprise that they are more hyper-connected and digitally savvy than their parents.
The combination of evolving educational needs for children and a more uncertain future of work means that updating what children learn, and how they learn it, has become a crucial issue for schools and colleges—but what should be prioritized?
Classrooms 2.0
In a survey of 1,400 educators, the majority of them say they believe that classrooms of the future will be centered around self-paced and personalized learning.
This student-centric approach would allow children to choose their own pace and learning objectives based on individual interests—all of which could be guided by artificial intelligence, chatbots, and video-based learning.
Artificial Intelligence
Artificial intelligence in education typically focuses on identifying what a student does or doesn’t know, and then subsequently developing a personalized curricula for each student.
The AI-powered language learning platform Duolingo is one of the most downloaded education apps globally, with more than 50 million installs in 2018. The platform single-handedly challenges the notion of traditional learning, with a study showing that spending just 34 hours on the app equates to an entire university semester of language education.
AI-driven applications in education are still in their infancy, but Duolingo’s success demonstrates the growth potential in the sector. In fact, the nascent market for AI in education is expected to reach $6 billion by the year 2025. Over half of this will come from China and the U.S., with China leading globally.
Chatbots
Chatbots are also quickly becoming a fundamental tool in next generation education. Designed to simplify the interaction between student and computer, chatbots provide a wide range of benefits, including:
- Spaced interval learning: Uses algorithms and repetition to optimize memorization
- Immediate feedback: Papers can be graded with 92% accuracy and in a faster time than teachers
- Self-paced learning: Tracks a student’s performance and guides them based on their individual needs
This innovative technology is arming educators with new strategies for more engaged learning, whilst simultaneously reducing their workload.
Video Learning
Although video-based learning may not necessarily be considered as innovative as artificial intelligence or chatbots, 98% of educators view it as a vital component in personalized learning experiences. Most institutions report incorporating video into their curriculums in some way, but even higher demand for video-based learning may come from students in the near future.
This is due to the fact that video learning increases student satisfaction by 91%, and student achievements by 82%, which could be why educators are increasingly using video for tasks like:
- Providing material for student assignments
- Giving feedback on assignments
- Flipped instruction (blended learning) exercises
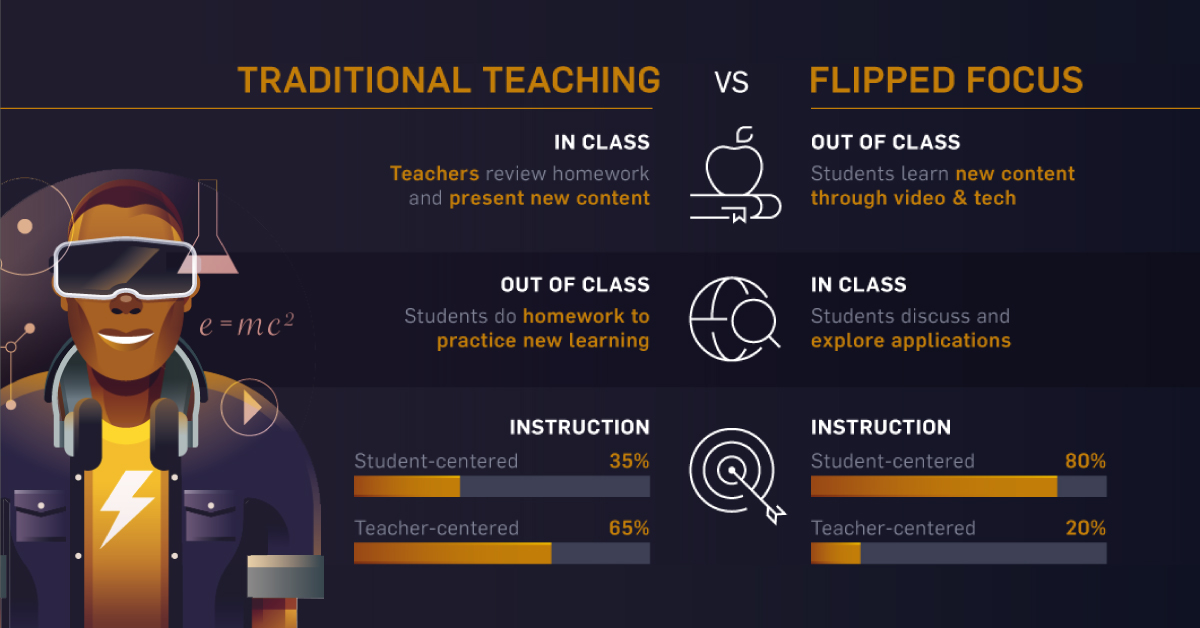
A flipped classroom overturns conventional learning by focusing on practical content that is delivered online and often outside the classroom.
The Battle Between Traditional and Tech
Flipping classrooms is a trend that has gained momentum in recent years—and may be considered to be a radical change in how students absorb information. The relatively new model also eliminates homework, by empowering students to work collaboratively on their tasks during class time.
Although new models of learning are disrupting the status quo of traditional learning, could the increasing amount of time children spend in front of screens be detrimental?
Research has shown that children are more likely to absorb information from books rather than screens. There has also been an evident increase in low-tech or tech-free schools that believe that human interaction is paramount when it comes to keeping children engaged and excited to learn.
Creating First-Class Humans
Although we may not be in the era of iTeachers just yet, the benefits of technology as teaching aids are undeniable. However, what is more important is that these aids are used in tandem with developmental and educational psychology—ultimately keeping students rather than technology at the core of education.
The future will be about pairing the artificial intelligence of computers with the cognitive, social and emotional capabilities of humans, so that we educate first-class humans, not second-class robots”
—OECD, Trends Shaping Education report
After all, how children develop these skills is perhaps less important than their ability to navigate change, as that is the only thing that will remain constant.
Technology
Charting the Next Generation of Internet
In this graphic, Visual Capitalist has partnered with MSCI to explore the potential of satellite internet as the next generation of internet innovation.
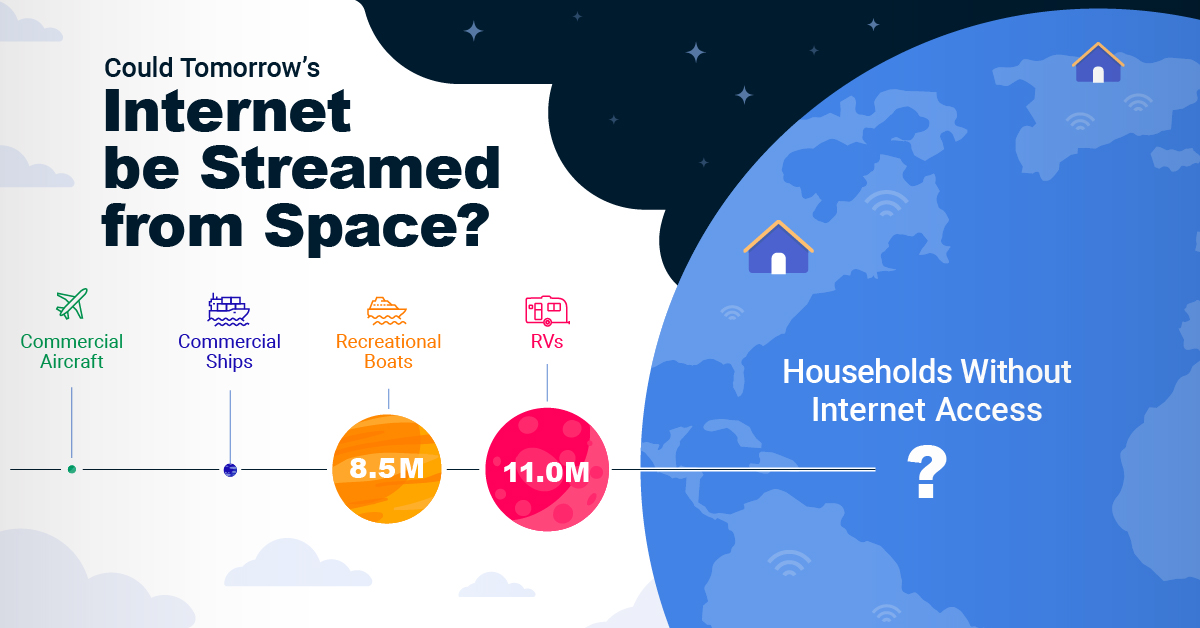
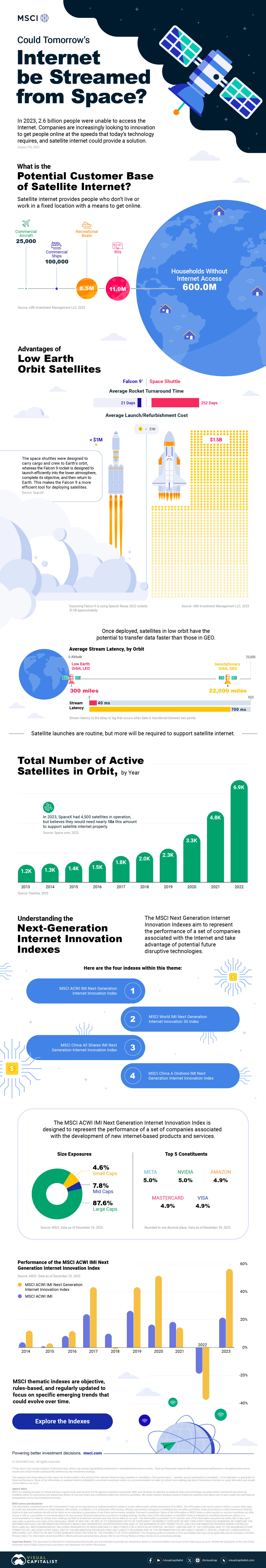
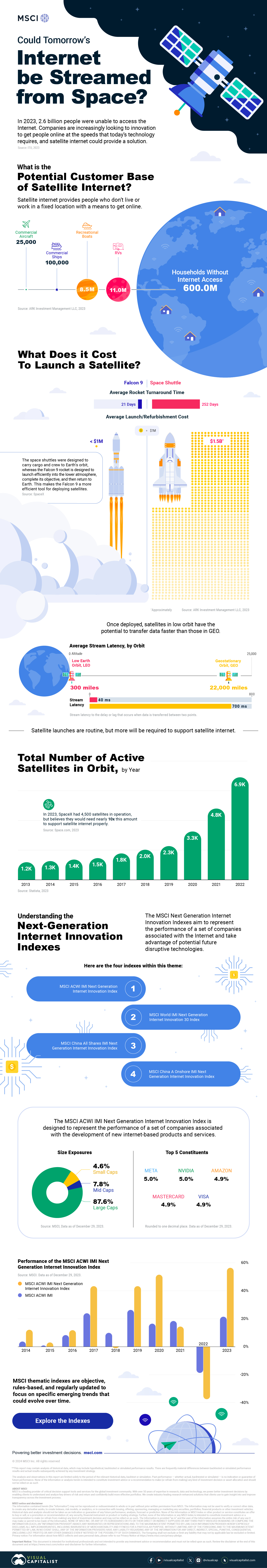
Could Tomorrow’s Internet be Streamed from Space?
In 2023, 2.6 billion people could not access the internet. Today, companies worldwide are looking to innovative technology to ensure more people are online at the speed of today’s technology.
Could satellite internet provide the solution?
In collaboration with MSCI, we embarked on a journey to explore whether tomorrow’s internet could be streamed from space.
Satellite Internet’s Potential Customer Base
Millions of people live in rural communities or mobile homes, and many spend much of their lives at sea or have no fixed abode. So, they cannot access the internet simply because the technology is unavailable.
Satellite internet gives these communities access to the internet without requiring a fixed location. Consequently, the volume of people who could get online using satellite internet is significant:
| Area | Potential Subscribers |
|---|---|
| Households Without Internet Access | 600,000,000 |
| RVs | 11,000,000 |
| Recreational Boats | 8,500,000 |
| Ships | 100,000 |
| Commercial Aircraft | 25,000 |
Advances in Satellite Technology
Satellite internet is not a new concept. However, it has only recently been that roadblocks around cost and long turnaround times have been overcome.
NASA’s space shuttle, until it was retired in 2011, was the only reusable means of transporting crew and cargo into orbit. It cost over $1.5 billion and took an average of 252 days to launch and refurbish.
In stark contrast, SpaceX’s Falcon 9 can now launch objects into orbit and maintain them at a fraction of the time and cost, less than 1% of the space shuttle’s cost.
| Average Rocket Turnaround Time | Average Launch/Refurbishment Cost | |
|---|---|---|
| Falcon 9* | 21 days | < $1,000,000 |
| Space Shuttle | 252 days | $1,500,000,000 (approximately) |
Satellites are now deployed 300 miles in low Earth orbit (LEO) rather than 22,000 miles above Earth in Geostationary Orbit (GEO), previously the typical satellite deployment altitude.
What this means for the consumer is that satellite internet streamed from LEO has a latency of 40 ms, which is an optimal internet connection. Especially when compared to the 700 ms stream latency experienced with satellite internet streamed from GEO.
What Would it Take to Build a Satellite Internet?
SpaceX, the private company that operates Starlink, currently has 4,500 satellites. However, the company believes it will require 10 times this number to provide comprehensive satellite internet coverage.
Charting the number of active satellites reveals that, despite the increasing number of active satellites, many more must be launched to create a comprehensive satellite internet.
| Year | Number of Active Satellites |
|---|---|
| 2022 | 6,905 |
| 2021 | 4,800 |
| 2020 | 3,256 |
| 2019 | 2,272 |
| 2018 | 2,027 |
| 2017 | 1,778 |
| 2016 | 1,462 |
| 2015 | 1,364 |
| 2014 | 1,262 |
| 2013 | 1,187 |
Next-Generation Internet Innovation
Innovation is at the heart of the internet’s next generation, and the MSCI Next Generation Innovation Index exposes investors to companies that can take advantage of potentially disruptive technologies like satellite internet.
You can gain exposure to companies advancing access to the internet with four indexes:
- MSCI ACWI IMI Next Generation Internet Innovation Index
- MSCI World IMI Next Generation Internet Innovation 30 Index
- MSCI China All Shares IMI Next Generation Internet Innovation Index
- MSCI China A Onshore IMI Next Generation Internet Innovation Index
MSCI thematic indexes are objective, rules-based, and regularly updated to focus on specific emerging trends that could evolve.

Click here to explore the MSCI thematic indexes

-
 Technology1 week ago
Technology1 week agoCountries With the Highest Rates of Crypto Ownership
While the U.S. is a major market for cryptocurrencies, two countries surpass it in terms of their rates of crypto ownership.
-
 Technology1 week ago
Technology1 week agoMapped: The Number of AI Startups By Country
Over the past decade, thousands of AI startups have been funded worldwide. See which countries are leading the charge in this map graphic.
-

 Technology3 weeks ago
Technology3 weeks agoAll of the Grants Given by the U.S. CHIPS Act
Intel, TSMC, and more have received billions in subsidies from the U.S. CHIPS Act in 2024.
-

 Technology3 weeks ago
Technology3 weeks agoVisualizing AI Patents by Country
See which countries have been granted the most AI patents each year, from 2012 to 2022.
-

 Technology3 weeks ago
Technology3 weeks agoHow Tech Logos Have Evolved Over Time
From complete overhauls to more subtle tweaks, these tech logos have had quite a journey. Featuring: Google, Apple, and more.
-

 AI1 month ago
AI1 month agoRanked: Semiconductor Companies by Industry Revenue Share
Nvidia is coming for Intel’s crown. Samsung is losing ground. AI is transforming the space. We break down revenue for semiconductor companies.
-

 Technology1 week ago
Technology1 week agoCountries With the Highest Rates of Crypto Ownership
-

 Mining6 days ago
Mining6 days agoVisualizing Copper Production by Country in 2023
-
 Politics7 days ago
Politics7 days agoCharted: How Americans Feel About Federal Government Agencies
-
 Healthcare1 week ago
Healthcare1 week agoWhich Countries Have the Highest Infant Mortality Rates?
-
 Demographics1 week ago
Demographics1 week agoMapped: U.S. Immigrants by Region
-
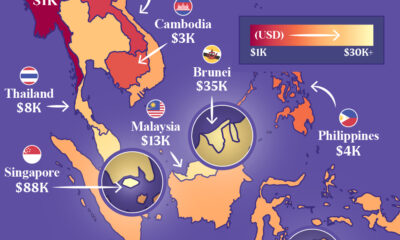
 Economy1 week ago
Economy1 week agoMapped: Southeast Asia’s GDP Per Capita, by Country
-
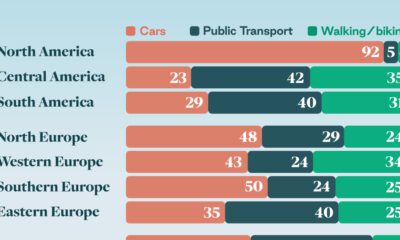
 Automotive1 week ago
Automotive1 week agoHow People Get Around in America, Europe, and Asia
-

 Personal Finance1 week ago
Personal Finance1 week agoVisualizing the Tax Burden of Every U.S. State